Web Store Demo
It’s time to actually build our store!
Data store
Let’s start with the DynamoDB tables. We’ll make three DynamoDB tables:
1. orders with order information
2. carts with cart information
3. products with product information
To create a table, from the AWS console, navigate to DynamoDB.

Then, on the DyanamoDB console, click on “Create Table”.
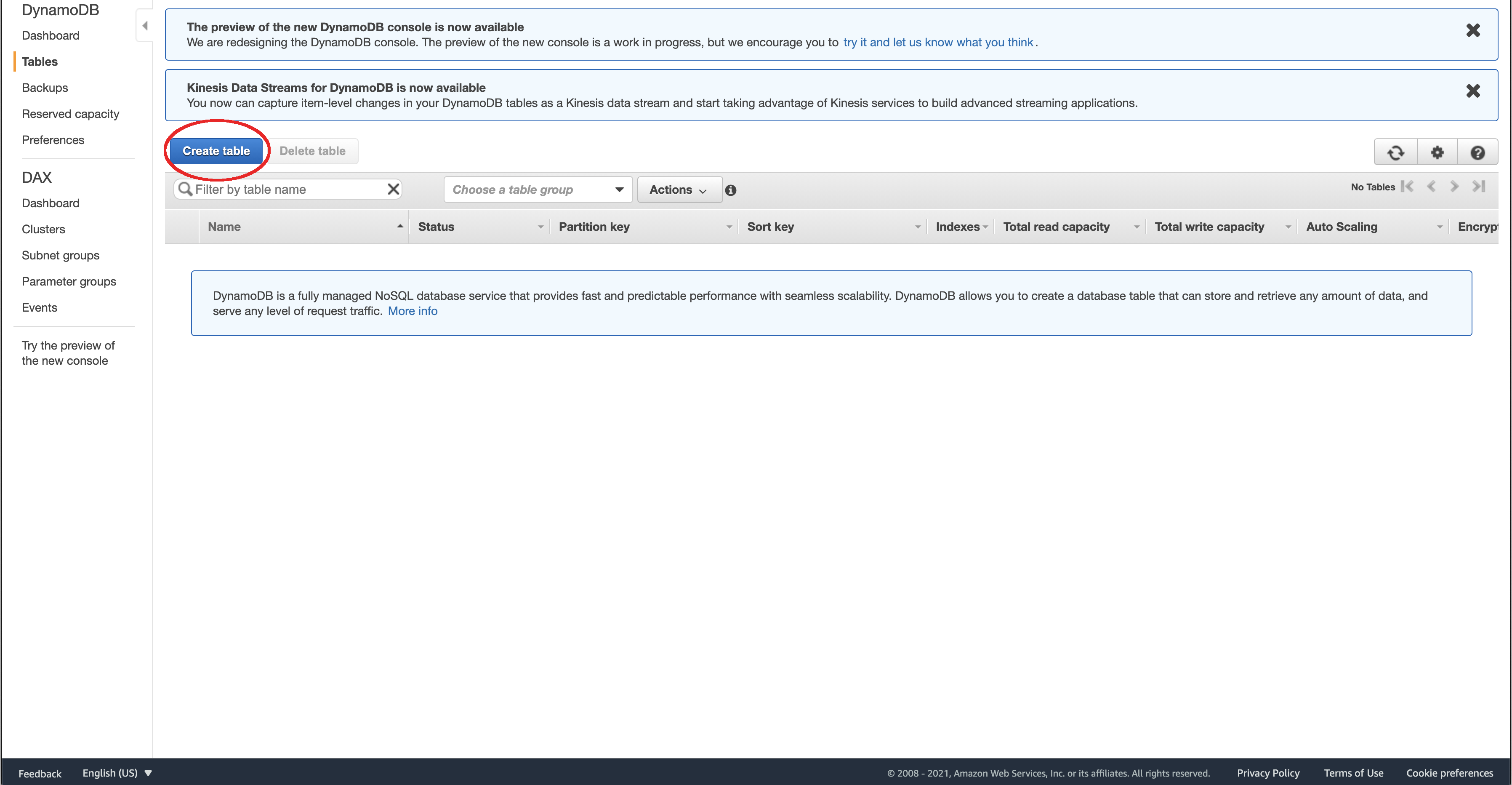
Fill in the table name with the name of your table and the Primary key.
The Primary key is like the key in a hash table, it’s the value that you would use to retrieve your value. In this example, I’ll be creating a table called orders with the key CustomerId, which will be my uuid representing a customer.
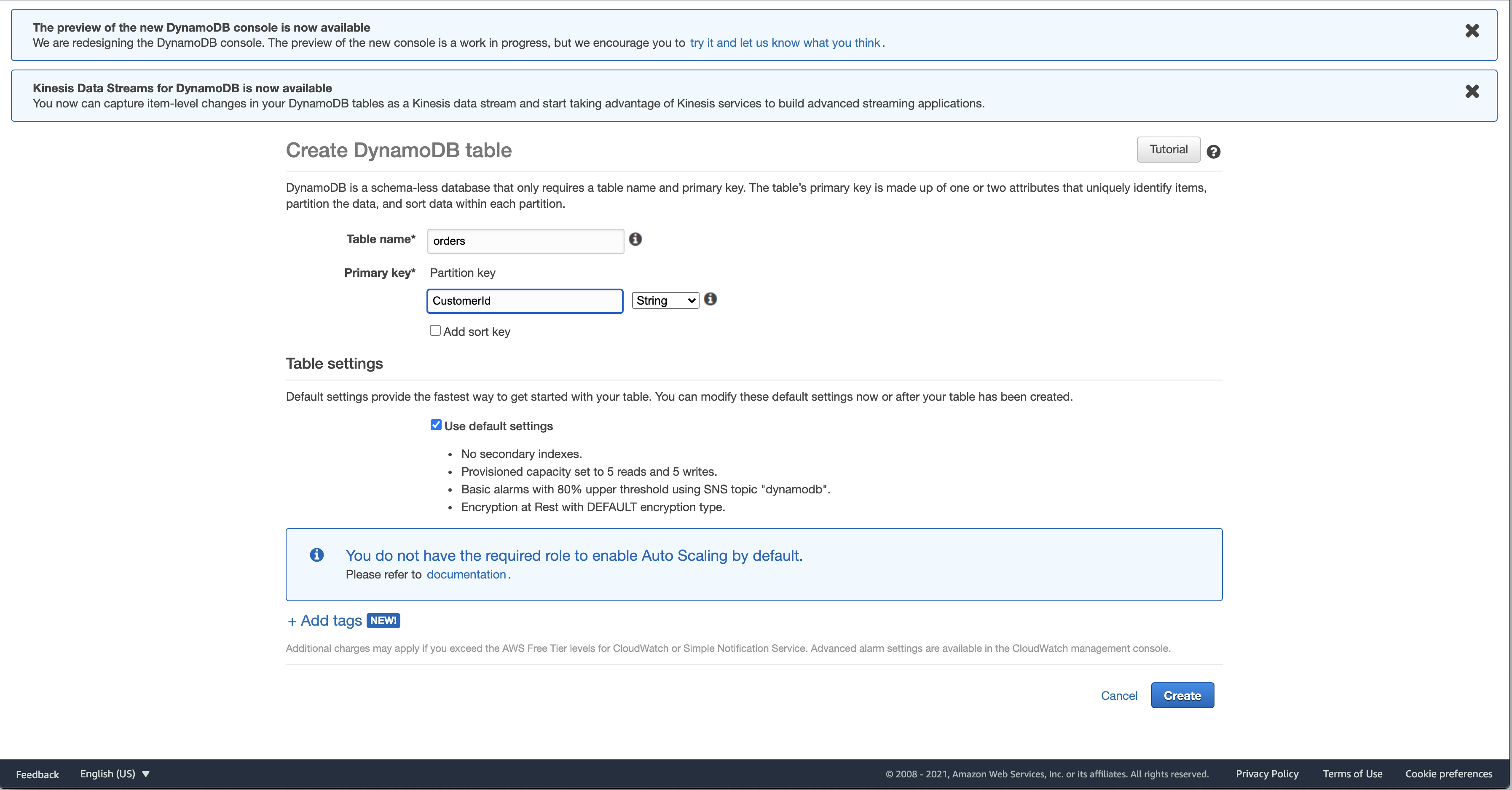 Click “Create”.
Click “Create”.
Repeat this process for our other tables as well.
carts should have CustomerId as the key, and products should have ProductId as the key
When you’re done, it should look like this:
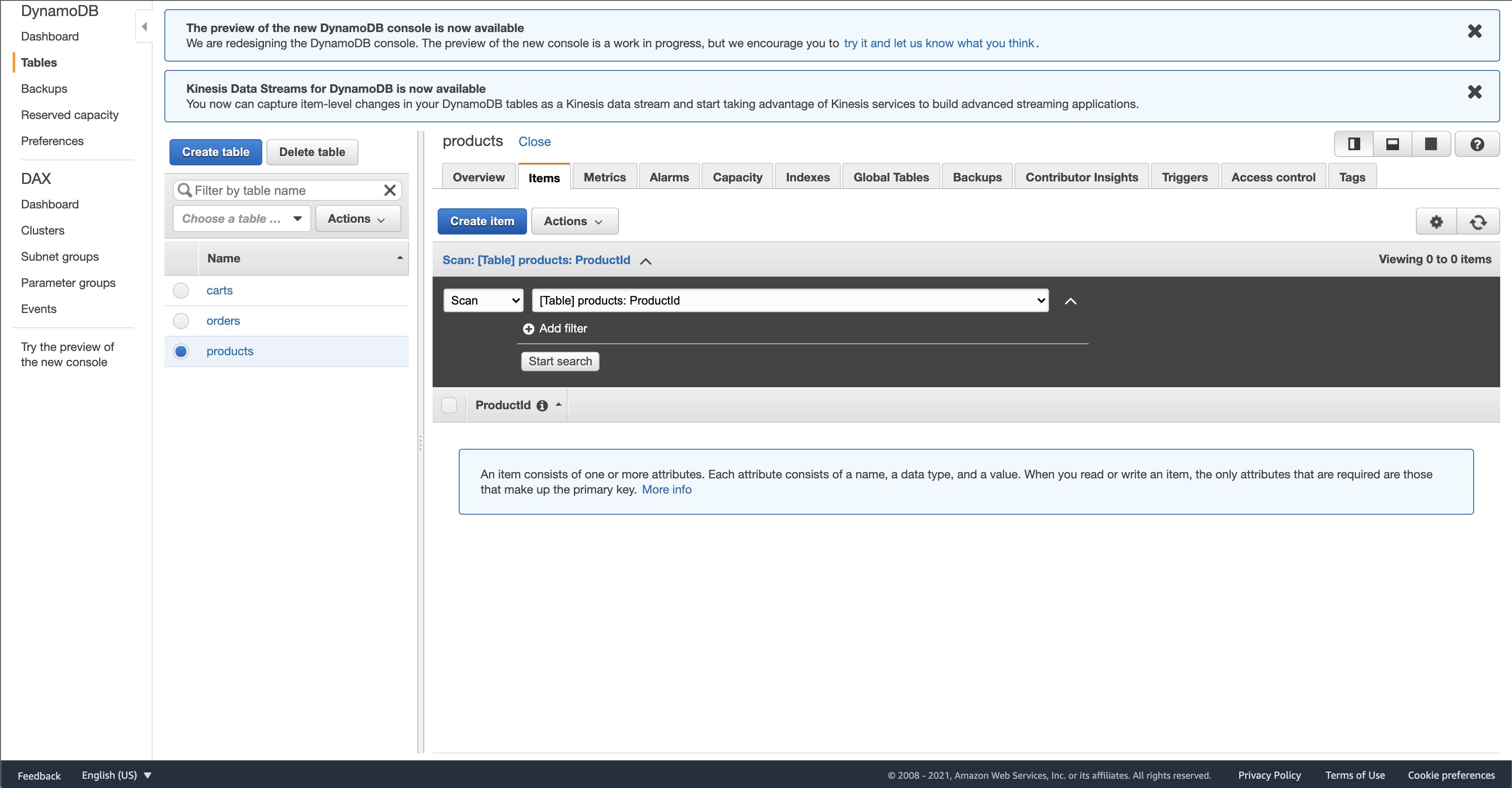
While we’re here, let’s add some books in the products table:
{
"Class": "COMP321",
"ProductId": "97b513ab-84f4-4d4f-b6fe-db8e0803789e",
"ProductName": "Types & Programming Languages"
}
{
"Class": "COMP211",
"ProductId": "f0d36b99-1e77-4e58-85d4-64c05d4a20fd",
"ProductName": "The C Programming Language"
}
{
"Class": "COMP112",
"ProductId": "f239b1b5-fb20-4812-856a-44a99970f52a",
"ProductName": "Think Python"
}
APIs
Now let’s create the APIs. I’ve decided to divide into three Lambda functions:
1. getProduct will be for querying product information;
2. cartHandler will be for querying cart information;
3. and makeOrder will be for making the orders
Create a Lambda
First, let’s create an execution role for our Lambda that can read our DynamoDBs
This step gives your Lambda permission to read and write from the DynamoDB tables that you created in the last step.
Go back to the AWS Console and look for IAM.

On the IAM Console, click “Roles” on the left.
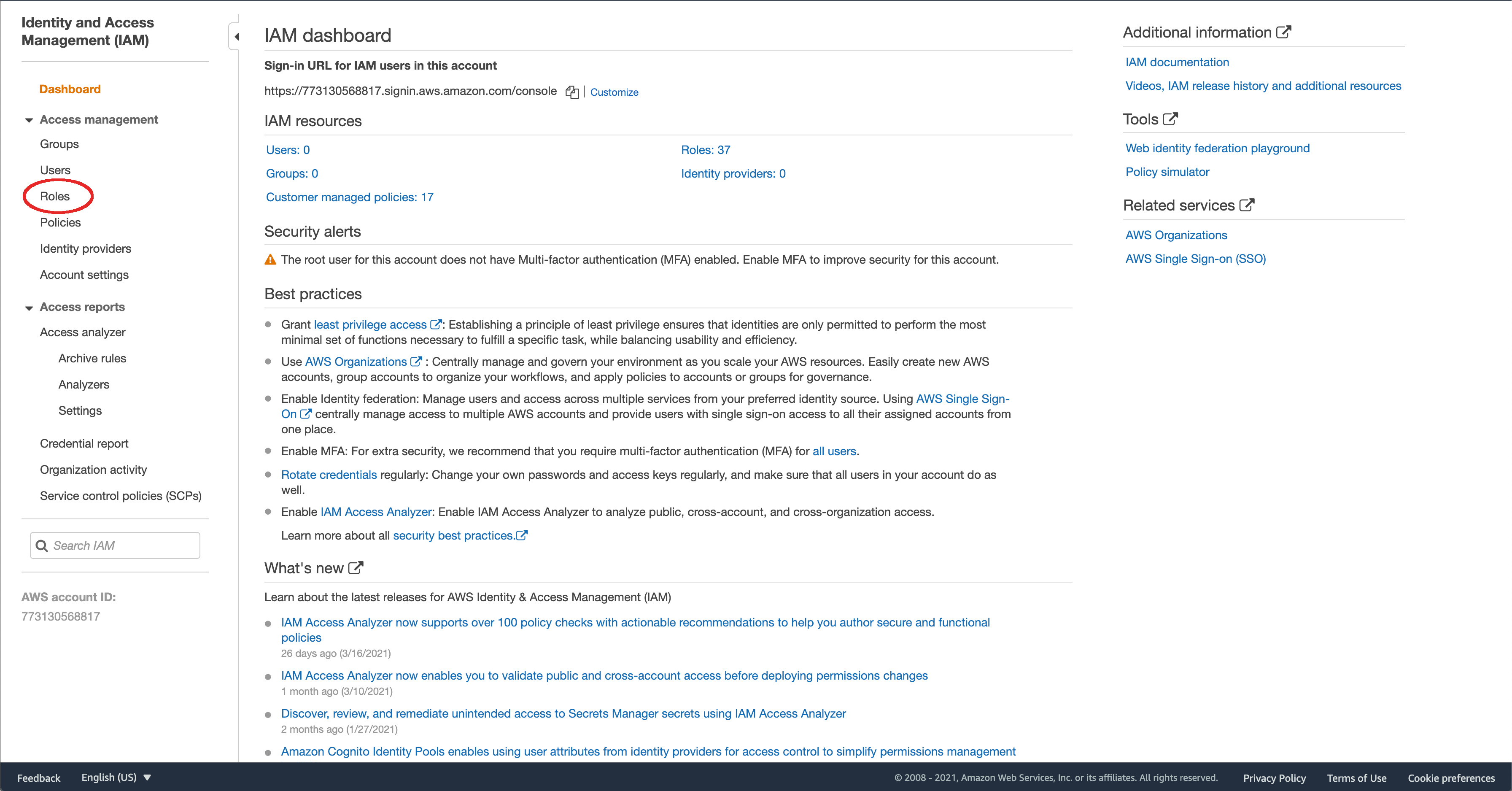 Click “Create Role”
Click “Create Role”
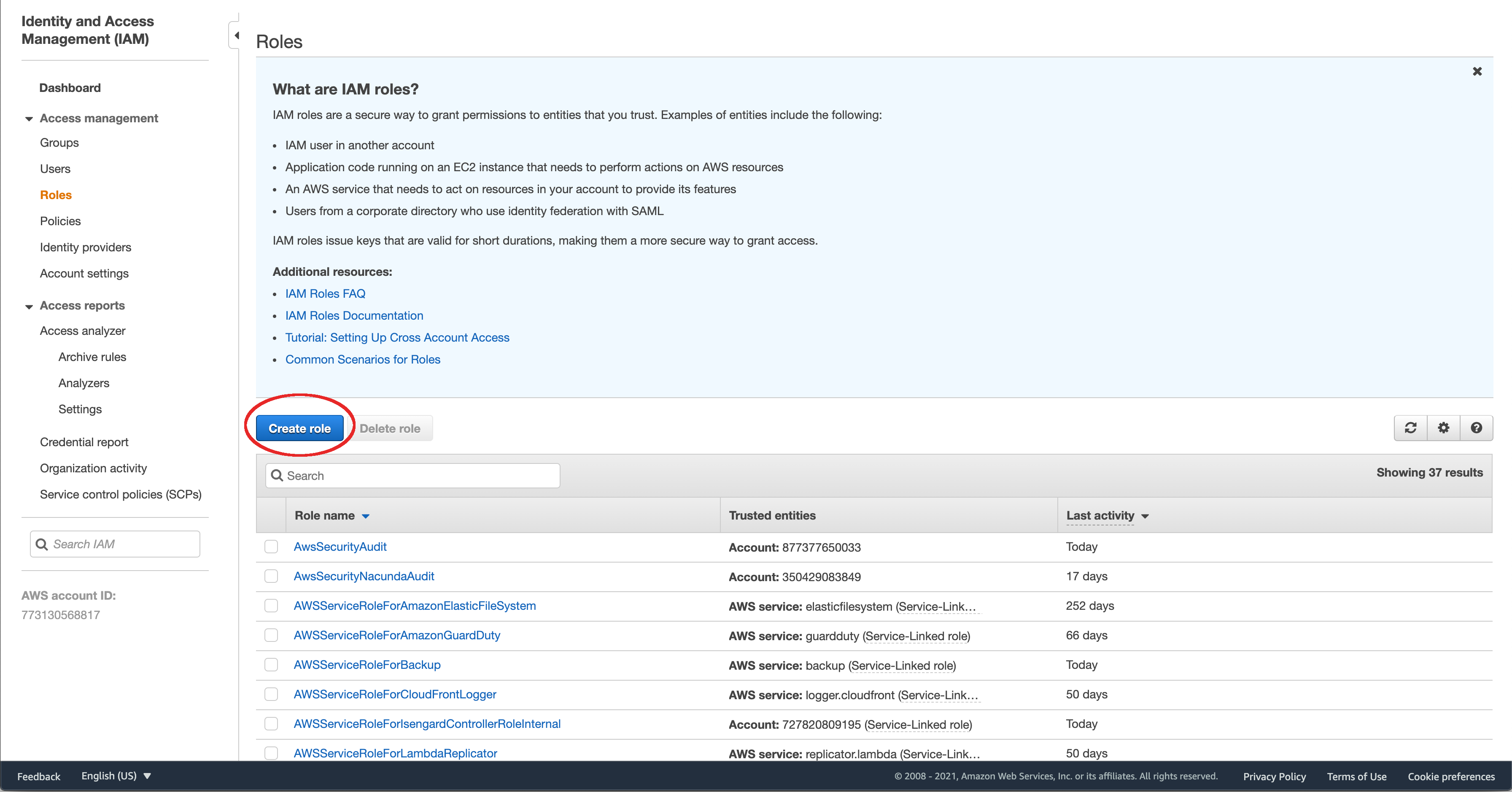 Select “AWS Service” as your trusted entity type and then “Lambda” under your use case. This allows Lambda to assume this role.
Select “AWS Service” as your trusted entity type and then “Lambda” under your use case. This allows Lambda to assume this role.
Click “Next”.
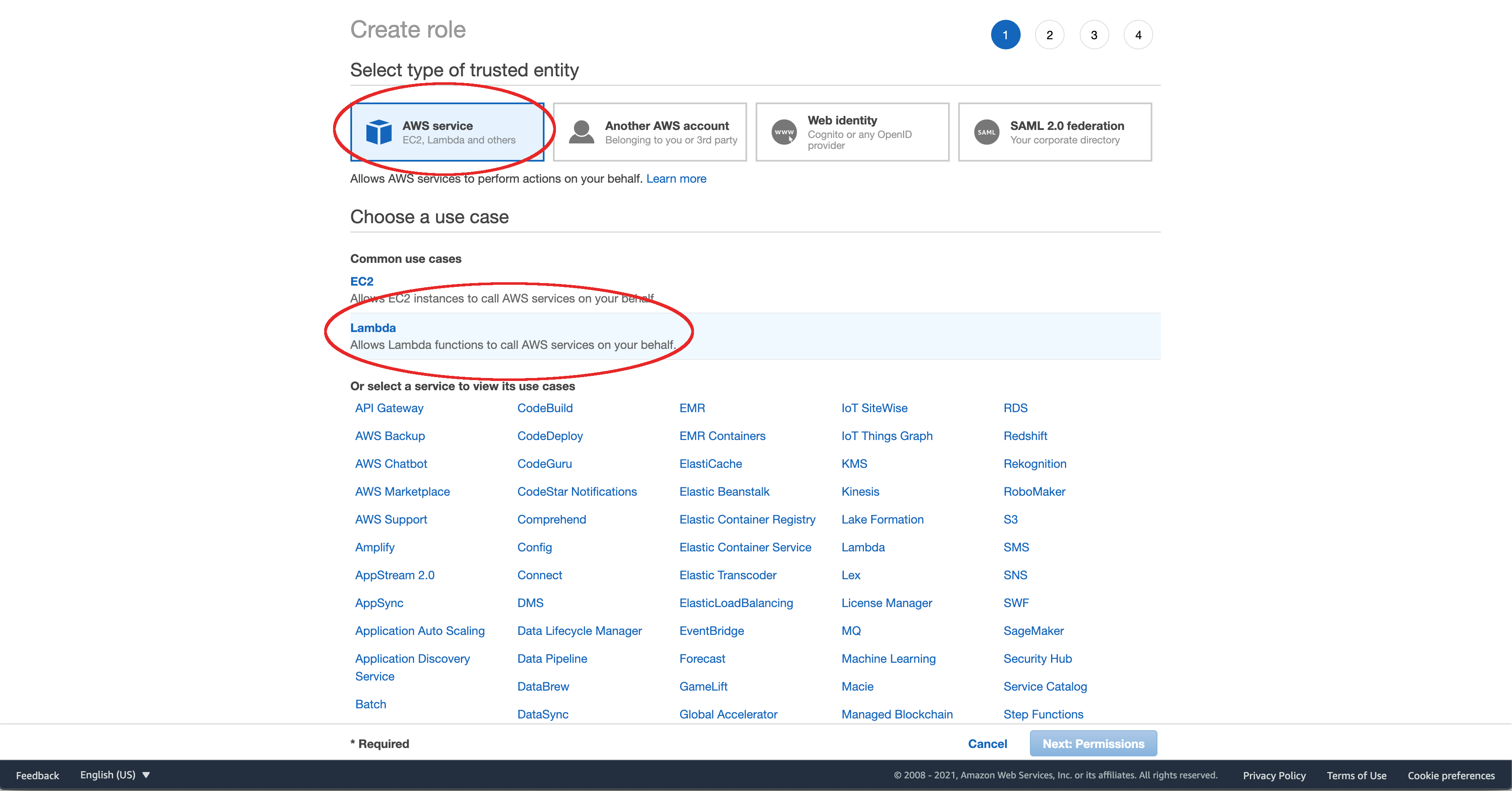
Enter dynamodb in filter policies, and select “AWSLambdaDynamoDBExecutionRole”. This step gives our Lambda the permission to read/write from DynamoDB and post logs to CloudWatch.
On the next page, you can add tags to your role, but you don’t have to do that. Just click next directly.
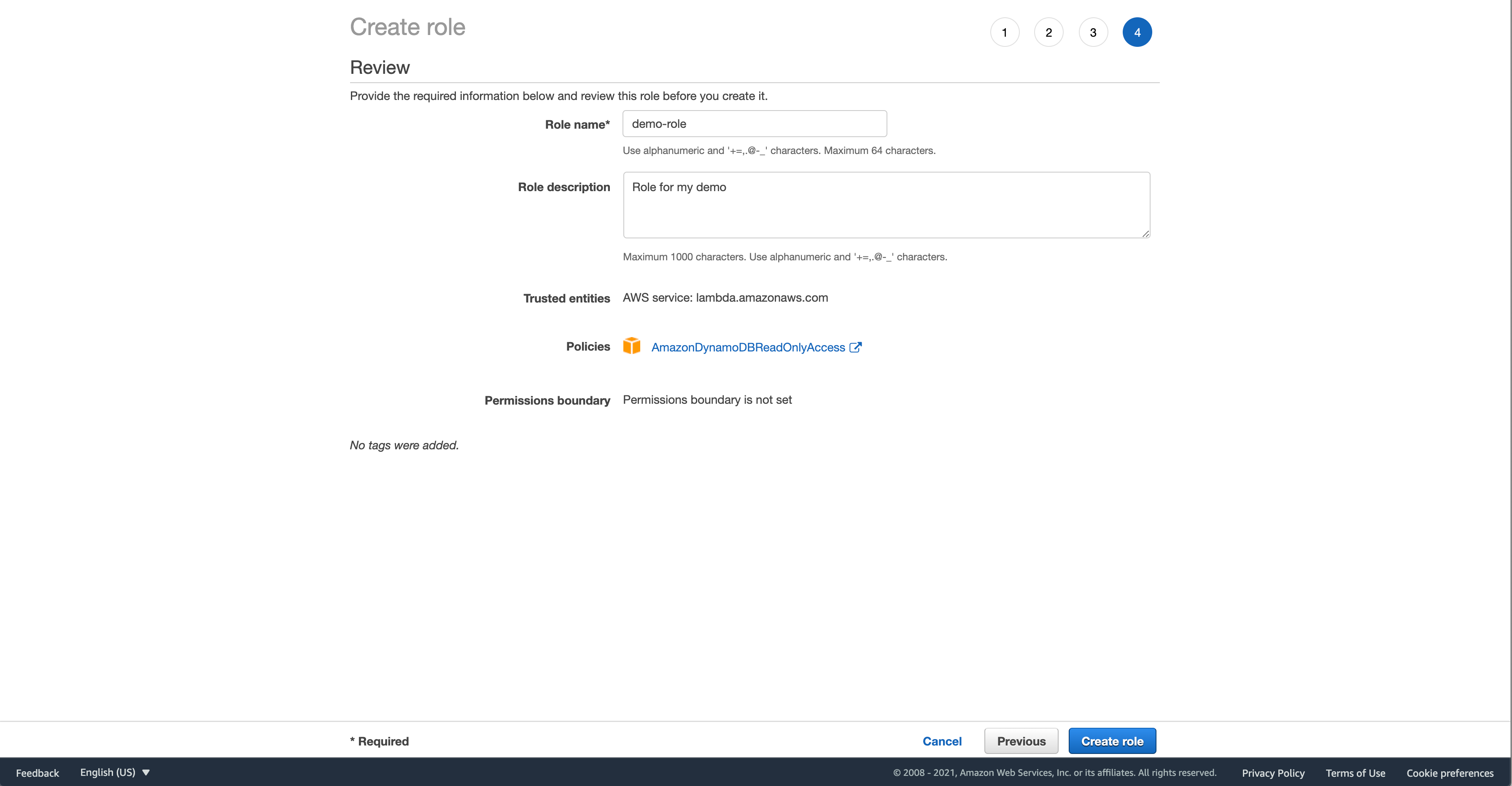
Then, on the fourth page, fill in a name for your role. I’m using “demo-role”. Note in my screen shot the policy is wrong. I had originally chosen that role but it ended up not logging correctly. Yours should say “AWSLambdaDynamoDBExecutionRole”. Click “Create Role”.
Create your Lambda
This is the fun part! Go back to the AWS Console and look for Lambda.
Click “Create Function”
The resulting page should look like this. You can click “Functions” on the top left to return to the Lambda Console.
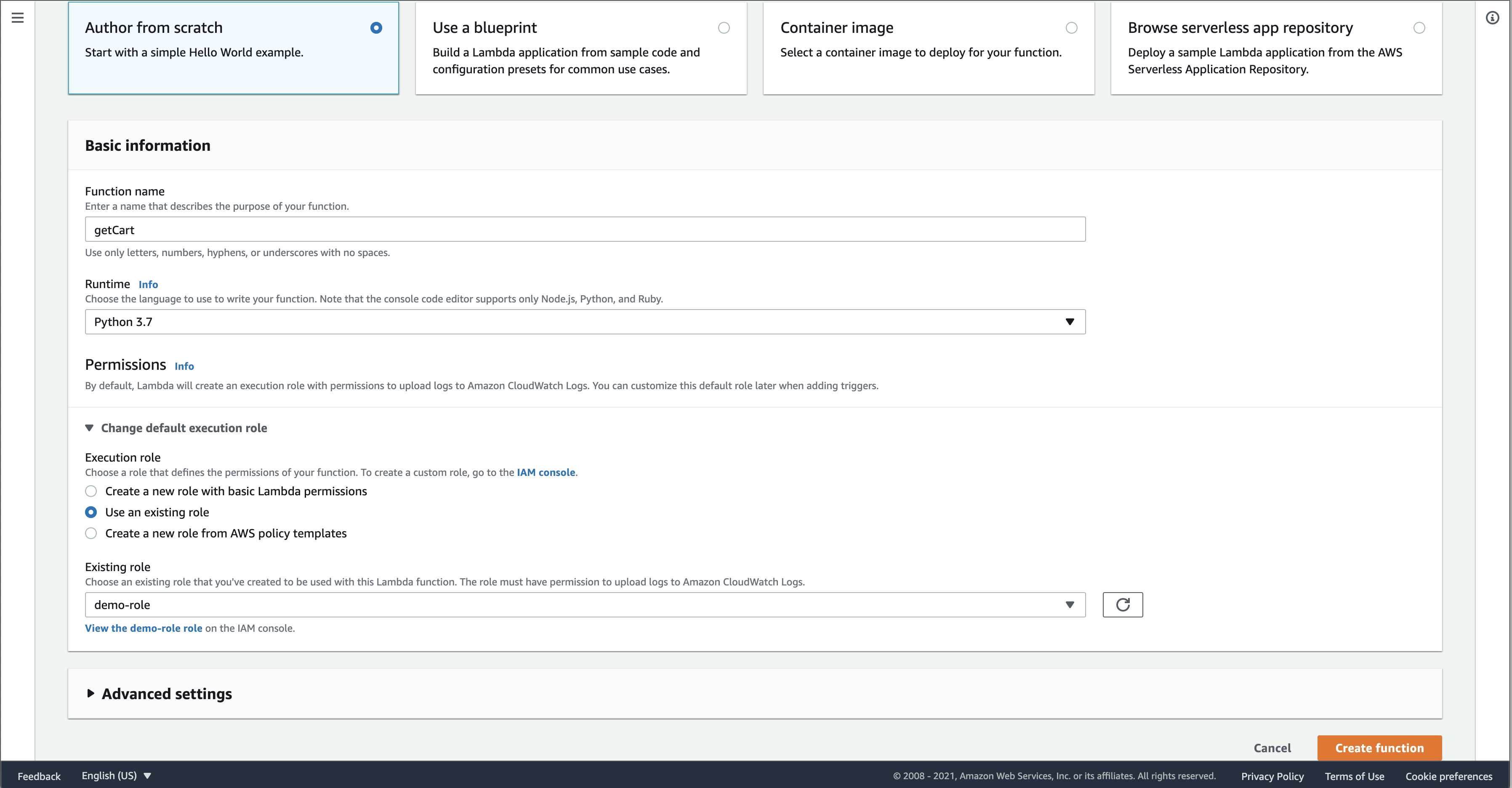
On this page, write a name for your function. I used getCart in this screenshot, but later renamed it to cartHandler, so you should use cartHandler to follow along with alter examples. For the runtime, I chose python 3.7. Then click the “Change default execution role” dropdown, and select “Use existing role”. Then in the “Existing role” dropdown, click demo-role. Click “Create Function”.
Repeat those create function steps again for the other two functions. Everything else should be the same but the function names should be getProduct and makeOrder.
Now click into getProduct.
Go ahead and copy my code into it.
import boto3
import json
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
products = dynamodb.Table("products")
def lambda_handler(event, context):
product = products.get_item(
Key={
"ProductId": event["pathParameters"]["ProductId"]
}
)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps(product)
}
in cartHandler, copy this code:
import boto3
import json
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
carts = dynamodb.Table("carts")
def lambda_handler(event, context):
customer_id = event["pathParameters"]["CustomerId"]
route_key = event["routeKey"]
try:
cart = carts.get_item(
Key={
"CustomerId": customer_id
}
)["Item"]
except KeyError:
cart = None
if route_key == "GET /cart/{CustomerId}":
print(cart)
if cart is not None:
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps(cart)
}
else:
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Items": []
})
}
elif route_key == "POST /cart/{CustomerId}/add/{ProductId}":
product_id = event["pathParameters"]["ProductId"]
if cart is None:
carts.put_item(
Item={
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Items": [product_id]
}
)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Items": [product_id]
})
}
else:
cart["Items"] += [product_id]
carts.put_item(
Item={
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Items": cart["Items"]
}
)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps(cart)
}
elif route_key == "POST /cart/{CustomerId}/remove/{ProductId}":
product_id = event["pathParameters"]["ProductId"]
new_items = [item for item in cart["Items"] if item != product_id]
carts.put_item(
Item={
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Items": new_items
}
)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Items": new_items
})
}
And finally, add this code in makeOrders:
import json
import boto3
import uuid
dynamodb = boto3.resource("dynamodb")
orders = dynamodb.Table('orders')
carts = dynamodb.Table('carts')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
route_key = event["routeKey"]
customer_id = event["pathParameters"]["CustomerId"]
try:
cur_orders = orders.get_item(
Key={
"CustomerId": customer_id
}
)["Item"]["Orders"]
except KeyError:
cur_orders = []
if route_key == "GET /orders/{CustomerId}":
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Orders": cur_orders
})
}
elif route_key == "POST /orders/{CustomerId}":
try:
products = carts.get_item(
Key={
"CustomerId": customer_id
}
)["Item"]["Items"]
except KeyError:
products = []
if products:
carts.put_item(
Item={
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Items": []
}
)
order = {
"Products": products,
"OrderId": str(uuid.uuid4())
}
cur_orders.append(order)
orders.put_item(
Item={
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Orders": cur_orders
}
)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({
"CustomerId": customer_id,
"Orders": cur_orders
})
}
else:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps({
"error": "Customer had no products to make an order"
})
}
Congrats! You’re done with Lambdas.
API Gateway
Now we need to create the router that routes from the web url to the lambdas. Go back to the AWS Console and look for “API Gateway”.

On the API Gateway console, choose “Build” under HTTP API.
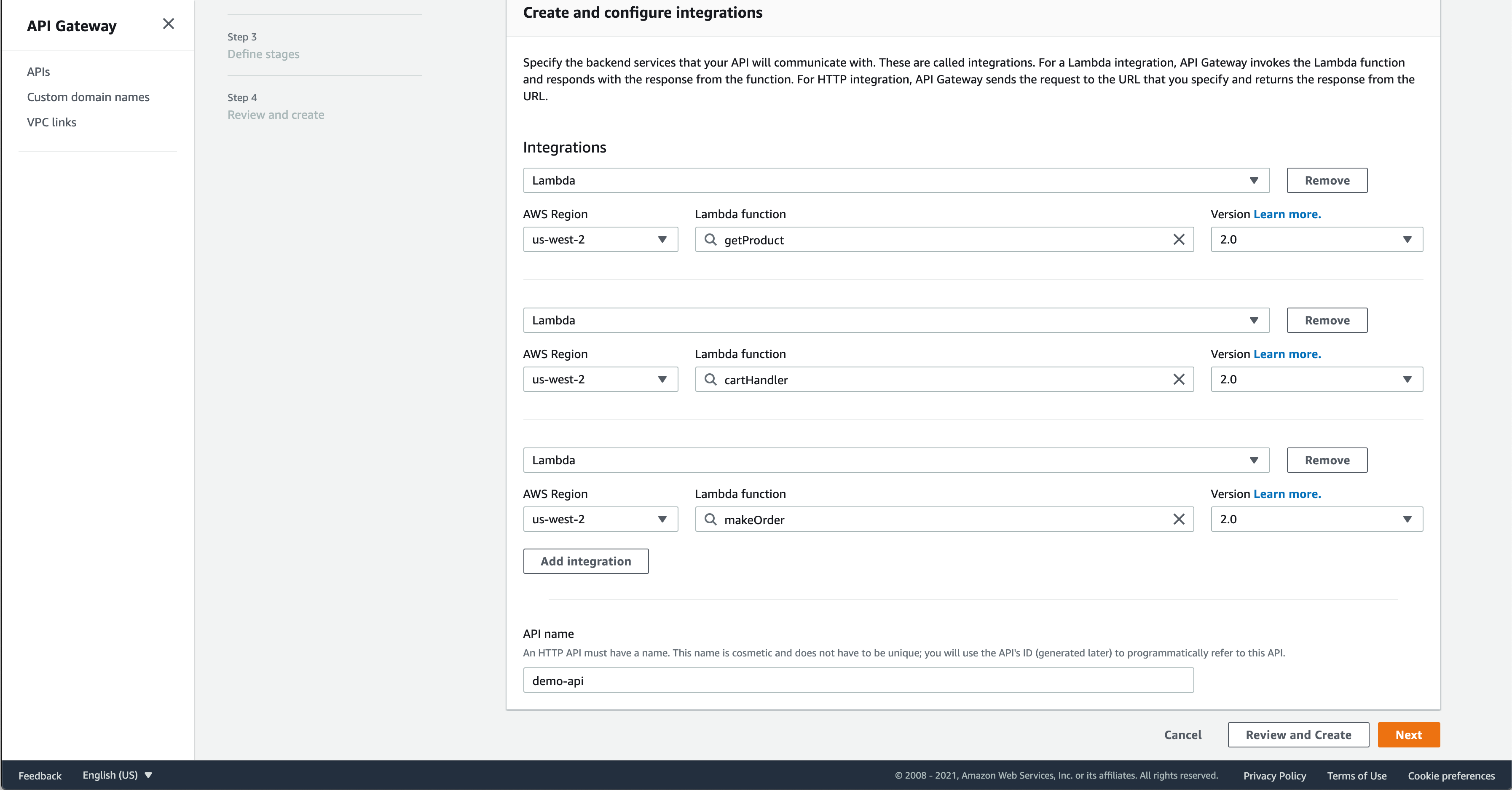
On the next page, choose add an integration. In the dropdown, pick “Lambda”. Then under Lambda function, select one of the Lambdas we’ve created. I chose getProduct first, but we need to add all three. Version 2.0 is the default version and seems to work fine.
For the API name, I chose demo-api. Click “Next”.
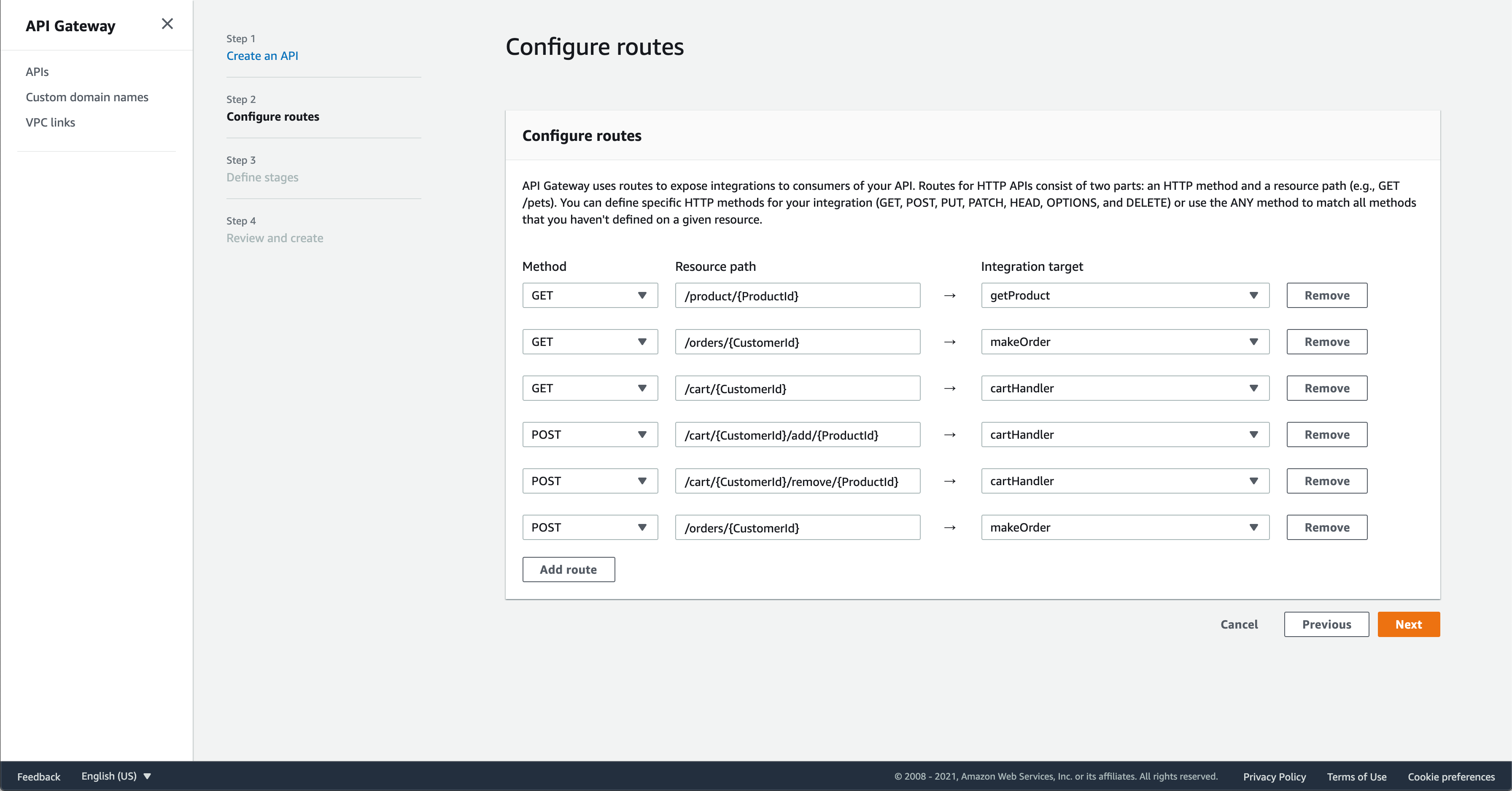
On this page, we will fill out the routes and where they point to. Add these six routes. Click “Next”.
On the next page, we don’t need to change anything. Click “Next”.
Then on the “Review and create” page, check that everything looks good and then click “Create”.
Now your API is ready to use.